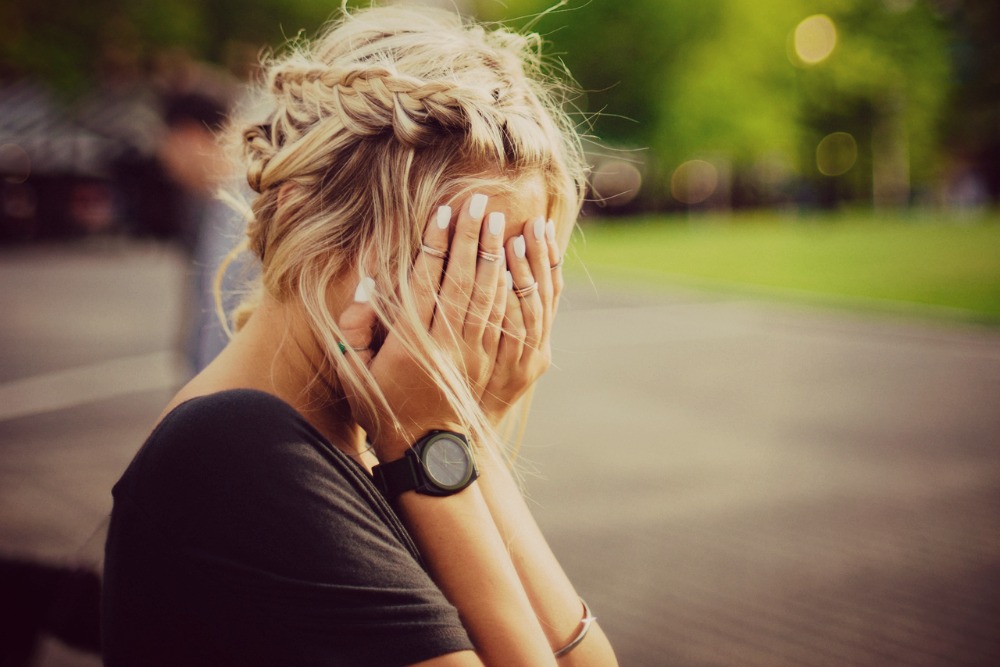
We all know the expression “butterflies in my stomach” and we all tend to agree on what that feeling signifies for us at a psychological level. We use this expression to describe feeling nervous, anxious, or excited. But did you know that the butterflies you feel in your “stomach” are actually representative of a complex and mutually reciprocal relationship between your brain and your gut?
There has been a growing understanding and exploration by psychologists, psychiatrists, physicians and researchers about the role our gut bacteria plays on our mood—most notably the experience of anxiety.
The stats.
The statistics on anxiety are staggering and trending north each passing year. Consider these stats: According to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (and NIMH) anxiety is the most common mental illness in America today.
An estimated 40 million adults (18 and older) or 18 percent of the population endorse symptoms of anxiety (not to mention one out of eight children). Treatment of anxiety accounts for one-third of the $148 billion dollars spent annually on mental illnesses in America.
In other words, we spend $42 billion a year on treatment of anxiety disorders in America. Women are 60 percent more likely to develop an anxiety disorder than our male counterparts. These numbers are terrifying to me as a clinician, a woman and a mother.
The gut-brain connection. How does it work?
The symbiotic relationship between our gut health and how we feel is a hot topic of discussion and research. Scientists, physicians, and mental health practitioners are increasingly aware of the important relationship between the balance of “critters” in our gut and how we experience our brain, mood and emotions. So, before we begin to discuss what we can do to optimize this important relationship, let’s explore the underlying processes.
From a holistic vantage point our gut is known as the “second brain” and there are structural/anatomical reasons for this reference. The “second brain,” known scientifically as the enteric nervous system, consists of sheaths of neurons located in the walls of our gut. We refer to these sheaths as the vagus nerve and it runs from our esophagus to our anus, roughly nine meters long.
- The bacteria, fungi and viruses that make up your body’s microflora outnumber your body’s cells by 10 to 1.
- 95 percent of the body’s serotonin supply is found in our bowels.
- The vagus nerve contains 100 million neurons, which is more neurons than the spinal cord or peripheral nervous system hold.
- There are over 100 trillion bacterial cells contained within the gut.
- Our gut sends far more information to our brain than the other way around.
When the precarious balance of bacteria in our gut becomes disturbed we often experience symptoms associated with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and other gastrointestinal related disorders. These symptoms are likely to start out as complaints of bloating, gas, constipation or diarrhea. When this occurs the domino effect of issues becomes inevitable and thus begins the cascading symptom patterns that plague tens of millions of Americans struggling with GI related disorders.
Due to the interconnectedness of our brain and enteric nervous system, via the vagus nerve, once our gut bacteria is out of whack, we are vulnerable to a pattern of emotional discomfort, usually marked by increasing episodes of anxiety and depression.
How does our gut bacteria become so unbalanced?
Here are a few of the many ways in which we accidentally (and sometimes unavoidably) contribute to this pattern of disturbance:
- Excessive and unmanaged stress;
- Too much use of antibiotics;
- Prolonged use of steroids
- Intestinal infections
- High sugar; low fiber diet (in other words, Standard American Diet (SAD))
- Regular consumption of alcohol
If you are reading this and you find yourself relating to this content, I encourage you to seek out professional help to better understand what these symptoms mean for your unique constitution.
The research.
There is a bourgeoning area of interest and research exploring the use of probiotics to treat a wide variety of mental illnesses. Pharmaceutical companies are attempting to create a new line of psychiatric medications referred to as Psychobiotics, but this field of research is still in its infancy.
There is a growing body of research that is exploring strain specific probiotics to help mitigate acute symptoms of anxiety. For example, in clinical trials involving the study of mice, Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus Rhamnosus have shown to help normalize anxiety-like behavior.
There are also a growing number of small human studies exploring the efficacy of using probiotics to combat anxiety symptoms. The preliminary data from these small studies echo the success from the rat-based research. In one study, 22 men reported feeling “less stress” after taking the strain specific probiotic for a month. Additionally, their lab results revealed lower levels of the stress hormone, cortisol while under duress. Both of these strains appear to work on the GABA receptors, an inhibitory neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of acute anxiety. GABA is the receptor influenced when you take a benzodiazepine such as Xanax or Ativan.
My emphasis within my clinical practice is to encourage my patients to explore the ways in which they can participate in healing their own bodies through the careful understanding of what their symptoms are telling them about their own unique emotional and physical constitution. Through seeking to find solutions that are rooted in personal empowerment, we start to shift our relationship to accountability, responsibility and personal growth. So, that being said, there is a lot we can do right from the comfort of our own home to start the process of realigning the balance of our gut flora. As you can imagine, most of it involves cleaning up our diet, being mindful of the relationship between food and mood, exploring our habits and patterns, and better metabolizing our emotions.
So, that being said, there is a lot we can do right from the comfort of our own home to start the process of realigning the balance of our gut flora. As you can imagine, most of it involves cleaning up our diet, being mindful of the relationship between food and mood, exploring our habits and patterns, and better metabolizing our emotions.
Listening To Your Gut. What can I do to heal my gut, mind and brain?
Below are action steps you can take in an effort to begin the process of healing your gut, mind and brain:It generally takes a minimum of 90 days for these suggestions to be effective:
It generally takes a minimum of 90 days for these suggestions to be effective:
- Eliminate sugars: The “fake” sugars. We are not talking about eliminating whole fruits. Rather, cutting out the baked goods, cookies, ice cream, and store bought sugary products that wreak havoc on the bacteria in our gut and lead to cyclical patterns of emotional and physical cravings.
- Eliminate all simple starches and reduce intake of even complex starches. The goal is to reduce the amount of yeast producing foods we consume.
- Reduce or stop drinking alcohol for the 90-day period. If this is difficult for you to do, observe the nature that “relationship.”
- Add in fermented and living foods. Please try to avoid store bought yogurts even though they are considered fermented. These products are loaded with sugars and often end up exacerbating imbalance.
- Consume copious amounts of veggies. Attempt to eat 6-9 cups of vegetables per day. Avoid use of store bought dressings etc., which are loaded with sugar and preservatives.
- Consume foods high in Omega-3 fatty acids (walnuts, salmon, flax, some types of squash, etc.).
- Aim to consume local and organic sources of animal protein. Doing so will reduce your ingestion of unwanted antibiotics and feed based chemicals.
- Discuss with your practitioner if the use of a probiotic or prebiotic will benefit your unique situation. A probiotic introduces specific strains of good bacteria, while a prebiotic introduces carbohydrates that serve as food the bacteria already present in your gut.
- Exercise. More days than not. Enough to sweat. The goal is to find joy in it. But if you hate it, that’s okay. Do it anyway.
- Drink mostly water.
- Work with a skilled psychologist or mental health professional to metabolize past trauma, identify faulty thought patterns, and implement mindfulness- based skills to better manage your central nervous system.
- Implement a daily mindfulness/meditation practice. The goal is observe your mind, not to clear it or control your thoughts. Simple observation and balanced breathing. This is a restful and restorative way to calm the central nervous system and recalibrate the vagus nerve. Mindfulness based relaxation has a myriad of benefits and has been shown to participate in changing neural pathways of emotional and physical pain. I suggest starting with a ten minute morning practice and increase it to twenty minutes once you feel the “mindfulness muscle” is more robust.
Exploring the relationship between our mood and our gut bacteria reveals an interconnected relationship between the mind, brain, and body, via the enteric nervous system and vagus nerve. This relationship is the foundation of why it is critical to address your emotional discomfort from a holistic and integrated approach to your wellness.
The good news is that because we now know and understand that there is a connection between the mind and body, we have the knowledge and tools to make immediate changes that will yield profound, albeit subtle results in how we feel. The better we understand and participate in our own sense of wellness and empowerment the more likely we are to embark on change that starts from within.
 About the Author: Dr Sarah Sarkis
About the Author: Dr Sarah Sarkis
She approaches psychological wellness from a holistic and integrative perspective. Her therapeutic style is based on an integrative approach to wellness, where she blends her strong psychodynamic and insight oriented training with more traditionally behavioral and/or mind/body techniques to help clients foster insight, change and growth. She has studied extensively the use of mindfulness, functional medicine, hormones, and how food, medicine and mood are interconnected. Her influences include Dr.’s Hyman, Benson, Kabat-Zinn and Gordon, as well as Tara Brach, Brene’ Brown, Irvin Yalom and Bruce Springsteen to name only a few.
Please visit her website at DrSarahSarkis.com and check out her blog, The Padded Room.
[irp posts=”1675″ name=”Our ‘Second Brain’ – And Stress, Anxiety, Depression, Mood”]



Thanks! Have you done any study on the effects of glysophate? It destroys gut bacteria and has been labeled a probable carcinogen by the World Health Organization. It is on/ and in most GMOs and is used to dry out most non organic grains. It has been suggested that glysophate might be responsible for the huge increase in gluten intolerence and other digestive disorders. Since most of our meat comes from animals fed GMOs, our meat is yet another problem. It is so wide spread that it is found in the blood and urine of most people as well as in breast milk. If you’re not familiar with Stephanie Senoff from MIT, she has done extensive research about glysohate and disease.
A very interesting article, especially the reference to the vagus nerve. The influence of the vagus (para-sympathetic innervation) is crucial in maintaining balance in the autonomic nervous system. Increasing vagal tone is the key part of Heart Rate Variability training; another excellent stress management technique. Thank you for putting together another piece of the puzzle. Keep up the good work.
Thank you! Such great information!
Excellent articles – well written and informative!!!!
Thank you!!!!!