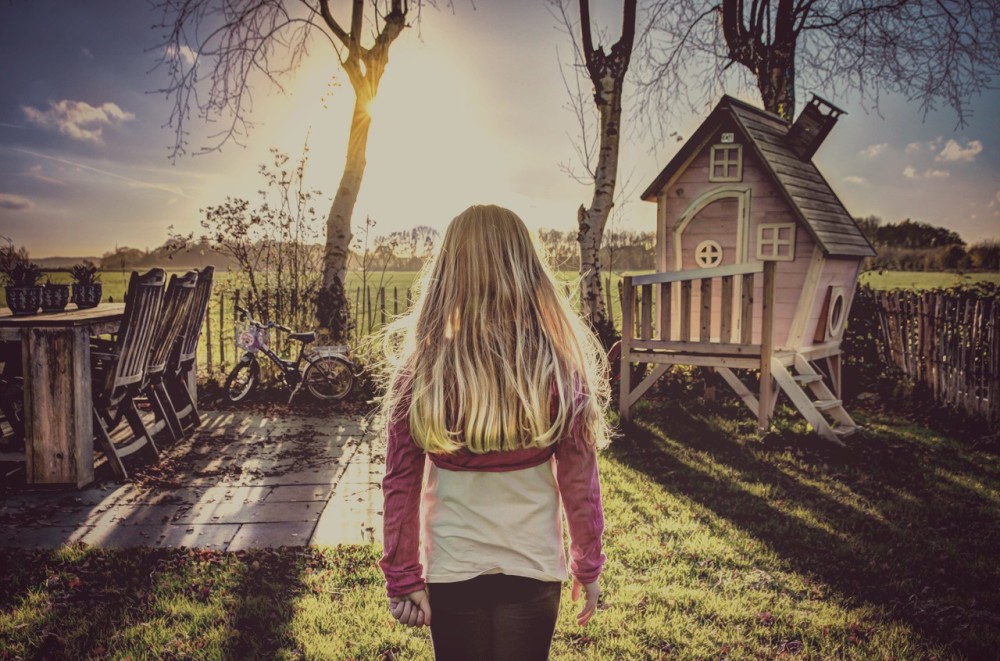
Stress is a normal part of life, and so is our response to it. The physiological response to stress is hardwired into all of us and is evolution’s way of keeping us alive. In times of stress, our heart beats faster, our blood pressure increases, and adrenaline and cortisol (the stress hormone) surge through our system to make us stronger, faster, more alert and more powerful versions of our normal selves. In short, the physiological changes that come with stress are to give us the physical resources to deal with whatever might break our stride.
But – the stress response was only ever meant to happen for brief periods of time. In the right doses, the cortisol (the stress hormone) that surges through the body in times of stress will help us to perform at our peak. When the cortisol is turned on and off quickly, it energises, enhances certain types of memory, and sets the immune system to go.
In a chronically stressful environment, the body’s stress response is always on – there is very little relief from the surge of chemicals and the increase in heart rate and blood pressure. When this happens, the stress becomes toxic and can cause dramatic changes in the brain and body – but there are ways to heal.
What is Toxic Stress?
Toxic stress isn’t so much about the cause of the stress, but about the chronic and ongoing nature of the stress.
Everyone will experience stress. It’s a very normal and healthy part of being human. For children though, a little goes a long way. It is through stressful times that kids learn resilience, determination, optimism and how to soothe themselves when things start to get tough. When stress is managed in the context of loving, stable and caring relationships, where children feel safe and secure, they can get through stressful, traumatic times without scarring.
The fallout from physical or emotional abuse and neglect is obvious, but then there are the more indirect hits, such as chronic conflict in the home, a parent battling addiction, maternal depression, or serious illness. The stress from these doesn’t have to turn toxic but it can. A prime conditions for this happening is when there is no loving, supportive, attentive relationship to buffer the impact. The relationship doesn’t have to be with a parent – any adult can make a powerful difference.
The brain, the body and toxic stress.
When the brain is constantly exposed to a toxic environment, it will shut down to protect itself from that environment. The brain continues working, but it’s rate of growth slows right down, creating a vulnerability to anxiety, depression and less resilience to stress.
Toxic stress affects people across all stages of the life span. The long-term effects will differ depending on the age of the person and the stage of brain development they are at when they are exposed to the stress.
The younger the brain, the more damaging the effects of toxic stress. A prenatal and early childhood brain is growing, developing and absorbing so much of what it is exposed to in the environment. This makes it incredibly vulnerable to chemical influences, such as stress hormones, which can cause long-term changes. Stress during this period will have broad impact, particularly on learning and memory.
Toxic stress during later childhood and adolescence will cause more problems for attention and impulse and emotional control, as these are the parts of the brain that are developing rapidly during this period.
During late adolescence or early adulthood, exposure to toxic stress will create a greater sensitivity to anything stressful and a more intense and enduring stress response.
Exposure to toxic stress during adulthood will intensify the ageing process and affect memory, cognition and emotion.
Here are some of the ways toxic stress can lay a heavy hand on the brain and the body. The degree to which toxic stress will cause damage depends on a number of things, including genetics, the availability of at least one strong, loving relationship to act as a buffer, and lifestyle factors that can potentially fortify the brain against the assault of toxic stress.
-
Learning, memory & emotion.
The experience of chronic poverty, neglect or physical abuse early in life seems to change the amygdala and the hippocampus. These are the parts of the brain that are vital for learning, memory and processing stress and emotion. A young brain is developing and strengthening connections all the time, and so it is particularly vulnerable to toxic stress. With toxic stress it’s a double hit – it gets in the way of the production of new connections, while at the same time reducing the connections that are already there. This compromises the architecture of the brain, weakening the foundation upon which all learning, behaviour and health will be built.
-
Increased vulnerability to addiction.
Addiction is a way of distracting from emotional pain and to avoid sitting in painful emotions. Addictive behaviour can provide temporary relief from physical pain and can blunt emotional and psychological pain. Research has found strong links between toxic stress and addictive behaviour, including the overuse of alcohol, tobacco and illicit drugs.
-
Over-reactivity and hypersensitivity to possible threat.
Experience changes the brain. The more a particular part of the brain is activated, the stronger and more active and permanent it becomes. When the threat response is continually triggered, both adults and children will develop a hypersensitivity to threat. This will play out with a tendency to misread ambiguous or non-threatening situations as threatening, a greater likelihood to sense anger or hostility (even when there is none), and the likelihood of being in a constant state of high alert, even in the absence of any real stress or threat.
-
Increased stress response as adults.
Research has found that even when adults have been long free of an abusive environment, there can be a greater tendency for everyday problems – traffic, arguments, disappointments – to trigger a heightened stress response. This can cause trouble for relationships and undermine physical and mental health. The abuse doesn’t have to be severe to have an effect. Physical abuse, whether mild, moderate or severe, resets the stress response to high and that’s where it stays.
-
Changes in DNA that persist through generations.
Research has found that when rats were exposed to toxic stress early in their lives, there were changes in a particular gene – the BDNF gene. The BDNF gene is involved in making a protein (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) found in the brain and spinal cord. This protein promotes the growth of new neurons and stops existing neurons from dying. It also has an important role in learning and memory, and is found in the parts of the brain that control eating, drinking and body weight. Low BDNF is associated with underdeveloped brain tissue. What’s worrying is that the changes in this gene that were found in the rats exposed to the toxic stress, were also found in their offspring, even though those offspring had not been exposed to toxic stress. This suggests that toxic stress changes the brain in ways that can be inherited, potentially creating vulnerabilities (not certainties) within following generations, whether or not those generations are exposed to toxic stress. It is important to remember that DNA is not destiny.
-
Greater vulnerability to mental illness.
In a meta-analysis of 16 studies involving more than 23,544 people, it was found that people with a history of chronic stress during childhood had double the likelihood of depression in adulthood. They also had a 43% higher chance of being non-responsive to therapy or medication. Of course, not all cases of depression have chronic childhood stress as their roots, but chronic stress can create a vulnerability. One of the reasons for this may be learned helplessness – the learning that nothing you do will make a difference to important needs being met.
-
Greater vulnerability to physical illness.
Chronic stress elevates the stress hormones which interfere with the functioning of the endocrine and immune systems. This has been associated with elevated inflammatory responses that can lead to auto-immune illnesses such as arthritis, allergies and asthma.
-
Migraines and chronic pain conditions.
Toxic stress during childhood is a significant risk factor for migraine. It is also associated with an earlier age of onset of migraine (16 years compared to 19 years). People exposed to abuse and neglect during childhood are more likely to have other pain conditions compared to those who have not been exposed to abuse. Specifically, research has found a link between emotional abuse and a greater prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome, chronic fatigue syndrome, and arthritis. Physical neglect has been associated with arthritis. For women, physical abuse has been associated with endometriosis, and physical neglect has been associated with uterine fibroids.
-
Compromised immune system.
The body’s stress response is activated within milliseconds of exposure to stress, but the immune system takes much longer to respond. This can be hours, sometimes days. When the stress is short-lived, even if it is intense, the immune system will not be affected. When the stress is more chronic and longer lasting, stress-related chemicals (cortisol, adrenaline) will keep surging through the body. Cortisol (the stress hormone) shuts down the capacity of the immune cells to respond to foreign invaders. When the release of cortisol is persistent, the immune cells don’t get the chance to recover. This means that when the body become invaded by viruses or infections, the immune system doesn’t have the heft it needs to fight them. Without anything to put up a fight, the body becomes an easy target for illness.
How to buffer the effects of toxic stress.
Chronic stress can’t always be avoided – the loss of a parent, an ugly divorce, conflict in the home, chronic maternal depression – but a relationship with an adult that is loving, responsive and stable can buffer against the effects of stress and stop it from turning toxic.
The environment might continue to be stressful and deeply painful for a child, but research has shown that with the support of a loving adult, the physiological effects of the stress response can be softened, minimising the risk of long-term damage.
A supportive adult can put stress into context by explaining how it happened, how often it will happen or whether it will happen again. This is an important part of helping a child to see the world as less threatening and to provide them with a sense of empowerment and the capacity to influence their environment, even if only in a very small way.
Never underestimate the importance one person can make to the life story of a child.
-
Build them up.
It is generally accepted that it takes 5-7 positive interactions to make up for a negative interaction. This is because our brains are wired to notice the negative (threats). It’s what keeps us alive. We will be quicker to notice the negative and will have a more intense response compared to positive events. Of course, interactions that are more disconnecting will take more of an ‘emotional topping up’ of the relationship. The more we can build kids up by giving them meaningful praise and opportunities to succeed and gain a sense of mastery, the more we can strengthen the pathways that help them feel positive emotions, deal with stress, and build their confidence.
-
Touch
Humans were meant to be touched. It’s connecting, reassuring and it helps to build a protective barrier between people and the things that could hurt them. We all need it. Deliberate hugs and incidental, safe touches will warm them and build them. Of course though, it’s also important to be guided by them. If they flinch or shy away from being touched, respect that.
-
Find them an escape.
If home is stressful, there needs to be some sort of temporary escape – for adults and children. A sport, a hobby, time with friends or other family will provide opportunities to relief from the emotional and physiological effects of the stress and validate personal strengths.
-
Be responsive.
We are all hardwired to connect with others. Children and babies will attempt to interact with the people who are important to them – it’s what we have been all biologically organised to do. Warmly responding to a child’s attempts at interaction – their babbling, reaching, crying or chatter – with eye contact, talking or hugging will strengthen the connections in the child’s brain and fortify them against toxic stress.
-
Strengthen the brain.
-
For a child, or an adult who has been exposed to toxic stress either as a child or in their current environment, anything that builds the brain will make a critical difference – diet, exercise, mindfulness, and connecting with a supportive, loving other. Strengthening the brain will help to put back what toxic stress takes out.
-
Mindfulness – for adults and children.
Research has found that mindfulness can protect adults against the effects of toxic stress from their childhoods. Mindfulness seems to provide some sort of resilience to the effects, improving the general well-being and helping them to be more effective with their own children. The risk of having a number of health conditions, such as depression, headache, or back pain, was almost halved in those with the highest levels of mindfulness compared with those who had the lowest. These findings stood even for those who had experienced several types of childhood adversity. (See here for a quick how to for mindfulness for adults and mindfulness for children.)
Genes and biology are NOT destiny – Turning around toxic stress.
Above all else, it is important to remember that biology and history are not destiny. Many of the effects of toxic stress can be reversed. The earlier toxic stress can be caught and met with a healthy response, the more effectively the healing from its effects. Relationships are key and healthy, supportive, stable ones have an extraordinary capacity to fortify people – children and adults – against the damaging effects of toxic stress. It’s the power of human connection, and it’s profound.



This is a great article. I just heard the term ‘toxic stress’ yesterday. I have had general anxiety since childhood. The source I have never really uncovered except a constant tension in the home over money amongst other things and a few traumatizing events. I don’t blame anyone. We all respond differently.
I have had insomnia since I was a baby and it got worse over the years. Medication has helped some but now…finally at age 40 after four days of no sleep and a serious enough accident… onset of menopause is making all of it worse. But I can say sleeping can be a huge help whether medicated or not.
In sum, things have really changed in the last few years. My job, being self-employed, environment, very demanding but no real up sides, and loss of any physical/ social outlet, adrenal exhaustion in 2012 ended my pro bike racing career/ I am so tired that socializing becomes a chore, the aggregate of stressors with no release, no positivity, and no one to trust, has created a state of chronic stress racheting up to anxiety atttacks now and it has affected my health greatly.
I am either working full speed or sick. It’s no life really. I am working on change but it’s not easy especially when yet another task feels not very stimulating.
I learned so much from this article. Sort of a road map out of the morass of sadness and pain that is my life. I am going to write each topic down and figure out what I can do now and what I need to work toward.
I do pray, try stay connected to family and friends, always try to be kind and grateful. No matter how bad things feel, I know there are others who are struggling more but we also construct our world with the words and thoughts we use and have.
Thank you for putting a well-organized, factual, self-guided publication out there that is not focused on selling yet more products or dispelling this connection between stress and the endocrine system as well as illustrating parallels bwt stress in esp in childhood and types of addiction that become a person’s actual safety or escape not because they are weak but because sometimes any fix feels better than nothing.
I hope you keep researching and writing because I think there are many people who relate to this and could use a structure to address and attempt to progress
Many thanks!
~M
What can I say without writing a book. I’m having an episode of toxic stress now. Blood work fine. Everything psychology is fine, the problem are the commodity. I eat a lot, fatigue to the point I can’t cat h my breath, pustular psoriasis internal. All because of abusive verbal relationships. I have an appointment with psychiatry tomorrow. Amen I found out about this. I’ve also been on antibiotics 6 months straight. Ugh
My toxic stress response has been re-activated at age 60, for my aged husband is trying to starve himself. I perceived that a friend blames me for my husband’s behavior. Tried to go to sleep with a racing pulse & rapid respiration.