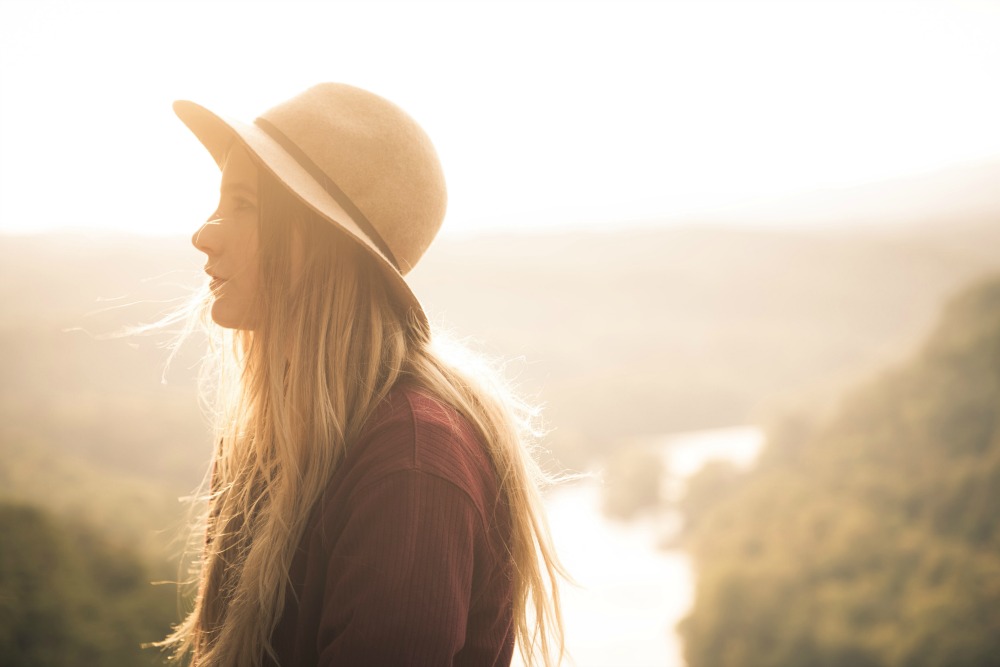
During adolescence, our teens will go through more changes than at any other time of their lives. Nothing will stay the same – their friendships, their bodies, their brains, their place in the world and the way they make sense of it. For many of them (and us!) there will be times it will feel confusing, exhausting and stormy.
During adolescence, the rates of depression show an alarming increase. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, in 2015, 12.5% of adolescents aged 12-17 had at least one major depressive episode.
There is so much that happens during adolescence that has the potential to widen the door just enough for depression to slip through and find its way to our teens. They will have friendship changes, their drive to experiment with their independence will see them feel a pull away from the warmth and protection of their family, and they will experience massive brain and body changes. As with all generations of adolescents, they will also be the first to have to negotiate many technological, global and social changes with much of the vulnerability of children, but with the world expecting them to behave like adults.
Whey are adolescents more vulnerable to depression?
One of the cruel things about depression is that it doesn’t need a reason to show up – sometimes it grabs on without any reason at all. Even with all the knowledge and readiness in the world, depression isn’t something we can always protect our teens against – it’s merciless like that – but the more we can understand and anticipate the risks for our teens, the more we can work to stop depression from making their path towards adulthood darker than paths were ever meant to be.
-
They’re becoming more sensitive to what others might be thinking.
As little people, our children are able to take the world as it comes, knowing that we’re by their side when things get tough. They don’t tend look outside of themselves for information about who they are meant to be. They just ‘are’. This is exactly how it’s meant to be for a while. They need to understand the world from their own perspective first, with themselves at the centre, and as they grow, their reference points and capacity to think of things from other perspectives will also start to grow.
As they move into adolescence, they will start to expand their capacity to see themselves through the eyes of another. With the social centres of the brain at full volume, and an increase in oxytocin, ‘the bonding hormone’, teens will tend to become more self-conscious – conscious of themselves – as they start to think about the kind of people they want to be, and how they can create the world they want to live in. This is a great thing but the downside is that it can make them sensitive to what other people might be thinking of them, particularly their peers.
Acceptance is important for any of us, but it becomes so much bigger during adolescence. Understandably, when the messages that are coming back to them – or the messages they think are coming back to them – aren’t nourishing and positive, it can bruise them from the inside out.
-
The pressures increase more than their brain power to deal with those pressures.
The demands of friends, family, school, future (who am I going to be?), sex, alcohol, drugs can be a confusing time. During adolescence, teens will experiment with their independence from us, as they look more to their peers for guidance and acceptance. This is normal and healthy and how it’s meant to be – but it’s hard. They’re travelling down a new and unfamiliar path, at a time when the drive towards independence will be pushing them to let go of the guard rails. This means they will be capable of wonderfully brave things, and they will see the world in new and interesting ways, but it will also set them up to take risks and feel persuaded to experiment with things that won’t always be good for them. Taking risks and experimenting can be a wonderfully brave, life-giving thing to do, or it can create fallout that can cause breakage.
-
Friendships – the good, the bad, the everything.
Friendships are vital for teens, but they can be fraught with heartache. As teens move into adolescence, they can become more vulnerable to exclusion, bullying and rejection – all at a time when feeling connected to peers becomes more important than ever. One of the main developmental goals of adolescence is independence from parents. As teens experiment with this, their need for connection with friends will increase. When teens are disconnected from their peers, intense and ongoing sadness, anger or self-doubt can carve open a vulnerability to depression.
-
Enough pillow time … or not.
The sleep cycle sees a big shift during adolescence. Melatonin, the hormone that makes us feel sleepy, is released about two hours later in teens than in adults. This means teens won’t even start to feel tired until about 10pm-ish. The melatonin stays in their system for about 8-10 hours, so if they wake up before that, they’ll feel the hangover of that. Early wakings are often unavoidable because of early school starts. Sadly, the body can’t store sleep so if your teen isn’t getting his or her 8-10 hours of sleep a night (and many of them aren’t), they might end up exhausted. When the lack of sleep becomes chronic, it can contribute to the vulnerability to depression. Sleep is when the brain sorts out its ‘emotional baggage’. Without it, emotional experiences can stay raw and unresolved. As well as this, a chronic lack of sleep can increase the levels of cortisol, the stress hormone in the body, which can also add to the vulnerability to depression.
-
Unhappy tummies.
The gut and the brain are deeply connected, so when teens start to diet or eat poorly, or binge on alcohol, the effect of this on the gut can cause problems for mental health. Inside the gut are billions of neurons that send information to the brain and directly influence feelings of stress, anxiety and sadness, as well as memory, decision-making and learning. Another reason a healthy gut is so important for mental health is because it’s the storehouse for 95% of the body’s serotonin – a neurotransmitter that is responsible for mood. Depression is widely attributed to a drop in serotonin, and many popular antidepressants work on restoring serotonin to healthy levels. We know that probiotics seem to alleviate the symptoms of anxiety and depression and this might be why.
-
The joy and the heartache that is social media.
Mobile phones and social media can open up their world in healthy, positive ways, but they can also open up the risk for cyberbullying and negative interactions – all of which can create a vulnerability to depression. Our teens are the first generation to move through adolescence with social media firmly by their side. They will find themselves having to learn tough lessons that we never had to. They are lessons about sexting, cyberbullying, and the capacity of the internet to make photos – and mistakes – accessible for everyone on the planet. Everyone. Forever. Our teens have the wisdom to navigate themselves through this, but not necessarily the desire to play it safe, or the ability to weigh up the positives and negatives consequences of their decisions. Technology can be a wonderful thing, or it can be a way for teens to really hurt themselves or each other.
-
A fierce pop culture that is relentless in telling who they should be, how they should be, and how they should look.
Research shows that when adolescent girls are shown idealised images of women, they become more unhappy with their bodies and more likely to feel depression, anxiety and anger. Increasingly, this is also becoming a problem for adolescent boys. Our teens are assaulted with images of ‘perfection’ everywhere they look. At a time when their bodies are changing, their skin is misbehaving, and they’re trying to figure out who they are and where they fit in to the world, it’s understandable that they might compare themselves to the glowing, confident, happy, carefree images they see in the media, and come out feeling ‘less than’. Even as adults we can fall into the trap. The risk is that eventually, they disconnect from their real selves and feel an emptiness and a loneliness, as they chase the ridiculously idealistic prescriptions for who they should be, how they should be, and how they should look.
Why are girls more at risk?
Girls are twice as likely to be diagnosed with a mood disorder as boys, but girls might be protected from greater harm because of their willingness to seek help and to talk things over with people close to them. Researchers aren’t certain about why the depression rates are escalating, particularly in adolescent girls, but they have a few very compelling theories:
-
Social media.
Girls tend to spend more time on social media sites, while boys more on gaming sites. Research in young adults has found that the more time they spend on social media, the greater the vulnerability to depression. There are a number of possible reasons for this:
> Social media tends to be saturated with images that can brew feelings of envy or inadequacy in the strongest of us.
> Social media has a way of evaporating time like it was never there. ‘I know I should shut it down, but just one more minute … okay, maybe five’. Playing around doing nothing in particular on social media can be fun – and we all need a bit of that – but too much can lead to too many feelings of having wasted time.
-
Differences in brain function between men and women.
Research has found that women are more sensitive to anything that has the potential to trigger negative emotions (such as negative images).
‘Not everyone’s equal when it comes to mental illness. Greater emotional reactivity in women may explain many things, such as their being twice as likely to suffer from depression and anxiety disorders compared to men,’ Adreanna Mendrek, associate professor at the University of Montreal’s Department of Psychiatry.
-
Body changes.
Girls generally go through the physical changes that come with puberty about two years before boys. Their changing bodies can trigger all sorts of feelings as they adjust to their new normal. Sometimes these will be positive, such as pride, excitement, anticipation, curiosity – and sometimes they won’t be.
And finally …
The only criteria for depression is being human. Depression is blind and unbiased and it doesn’t care who it targets – it really can happen to anybody. For some reason, probably plenty of reasons, depression seems to flourish during adolescence. At a time when the world starts opening up to our teens, for too many of them, the world shuts down. Our teens deserve to thrive, and feel the ‘aliveness’ that comes with the learning and discovery that comes with the adventure towards adulthood. By being aware of the risk factors for depression, we can work to limit those risks for our teens as much as we can, and support their courageous, strong reach into the world.
[irp posts=”3915″ name=”Depression in Teens: The Warning Signs and How to Help Them Through”]



We should remember that if everybody said nothing…there really would be chaos.
“All it takes for Evil to flourish…is for One Good Person to say Nothing”…Anon
Thanks so much for this valuable information. Sometimes, we notice that something is bothering a family member, but don’t like to ‘butt in’ and bring the subject up…for fear of being a ‘sticky beak’. I will simply print off and send in the mail.
Sort of a long-distance Sticky Beak.
Regards,
Cindy
This article is helpful for all parents with preteens as well as teens being cared for
We only need to realize that for a preteen or teen in Foster Care the above sections are intensified greatly by the “Forced” or needed living situations that they are in.